学习C – C break
我们可以使用break语句退出for循环。
此示例计算任意数量值的平均值:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h> // For tolower() function
int main(void)
{
char answer = "N"; // Decision to continue the loop
double total = 0.0;
double value = 0.0;
unsigned int count = 0;
for( ;; ) // Indefinite loop
{
printf("\nEnter a value: "); // Prompt for the next value
scanf(" %lf", &value); // Read the next value
total += value; // Add value to total
++count; // Increment count of values
// check for more input
printf("Do you want to enter another value? (Y or N): ");
scanf(" %c", &answer); // Read response Y or N
if(tolower(answer) == "n") // look for any sign of no
break; // Exit from the loop
}
// Output the average to 2 decimal places
printf("\nThe average is %.2lf\n", total/count);
return 0;
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

例子
使用break退出循环
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
float length, width;
printf("Enter the length of the rectangle:\n");
while (scanf("%f", &length) == 1)
{
printf("Length = %0.2f:\n", length);
printf("Enter its width:\n");
if (scanf("%f", &width) != 1)
break;
printf("Width = %0.2f:\n", width);
printf("Area = %0.2f:\n", length * width);
printf("Enter the length of the rectangle:\n");
}
return 0;
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

例2
使用switch语句和break
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int main(void)
{
char ch;
printf("Please type in a letter; type # to end.\n");
while ((ch = getchar()) != "#")
{
if("\n" == ch)
continue;
if (islower(ch)) /* lowercase only */
switch (ch)
{
case "a" :
printf("a\n");
break;
case "b" :
printf("b\n");
break;
case "c" :
printf("c\n");
break;
case "d" :
printf("d\n");
break;
case "e" :
printf("e\n");
break;
case "f" :
printf("f\n");
break;
default :
printf("That"s a stumper!\n");
} /* end of switch */
else
printf("only lowercase letters.\n");
while (getchar() != "\n")
continue; /* skip rest of input line */
printf("Please type another letter or a #.\n");
} /* while loop end */
return 0;
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。
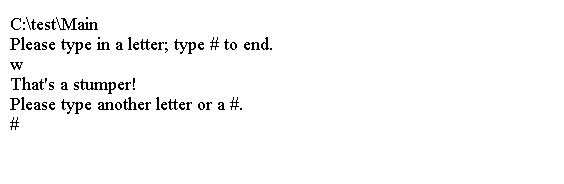

 国外主机测评 - 国外VPS,国外服务器,国外云服务器,测评及优惠码
国外主机测评 - 国外VPS,国外服务器,国外云服务器,测评及优惠码








