学习C++ – C++构造函数
类构造函数是类中的一种特殊类型的函数。
当定义类的新实例时调用构造函数。
它在创建新对象时初始化,并确保数据成员包含有效值。
类构造函数与类具有相同的名称。
Box(),例如是Box类的构造函数。
构造函数不返回值,因此没有返回类型。
如果您没有为类定义构造函数,编译器将提供默认构造函数。
用new对象初始化
一般来说,如果Class_name是一个类,如果value的类型为Type_name,则该语句
Class_name * pclass = new Class_name (value);
调用此构造函数:
Class_name (Type_name);
可能有微小的转换,例如:
Class_name(const Type_name &);
例子
实例化MyBook类的多个对象,并使用MyBook构造函数指定每个MyBook对象创建时的课程名称。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class MyBook {
public:
// constructor initializes courseName with string supplied as argument
MyBook( string name ) {
setCourseName( name ); // call set function to initialize courseName
}
// function to set the course name
void setCourseName( string name )
{
courseName = name; // store the course name in the object
}
// function to get the course name
string getCourseName()
{
return courseName; // return object"s courseName
}
// display a welcome message to the MyBook user
void displayMessage()
{
// call getCourseName to get the courseName
cout << "Welcome to the grade book for\n" << getCourseName()
<< "!" << endl;
}
private:
string courseName; // course name for this MyBook
};
int main() {
// create two MyBook objects
MyBook MyBook1( "C++ Programming" );
MyBook MyBook2( "C++" );
// display initial value of courseName for each MyBook
cout << "MyBook1 created for course: " << MyBook1.getCourseName()
<< "\nMyBook2 created for course: " << MyBook2.getCourseName()
<< endl;
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

复制构造函数
复制构造函数的形式对于任何类是相同的:
Type::Type(const Type& object)
{
// Code to duplicate of object...
}
例2
默认构造函数没有参数,唯一的目的是允许创建一个对象。
class Box
{
private:
double length {1};
double width {1};
double height {1};
public:
// The default constructor that is supplied by the compiler...
Box()
{
// Empty body so it does nothing...
}
// Function to calculate the volume of a box
double volume()
{
return length*width*height;
}
};
例3
以下代码为Box类添加构造函数。
#include <iostream>
// Class to represent a box
class Box {
private:
double length {1.0};
double width {1.0};
double height {1.0};
public:
// Constructor
Box(double lengthValue, double widthValue, double heightValue)
{
std::cout << "Box constructor called." << std::endl;
length = lengthValue;
width = widthValue;
height = heightValue;
}
// Function to calculate the volume of a box
double volume()
{
return length*width*height;
}
};
int main()
{
Box firstBox {80.0, 50.0, 40.0}; // Create a box
double firstBoxVolume {firstBox.volume()}; // Calculate the box volume
std::cout << "Volume of Box object is" << firstBoxVolume << std::endl;
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

定义类之外的构造函数
函数成员的定义可以放在类定义之外。
类构造函数也是如此。
#include <iostream>
class Box {
private:
double length {1.0};
double width {1.0};
double height {1.0};
public:
// Constructors
Box(double lengthValue, double widthValue, double heightValue);
Box(); // No-arg constructor
double volume(); // Function to calculate the volume of a box
};
// Constructor definition
Box::Box(double lengthValue, double widthValue, double heightValue)
{
std::cout << "Box constructor called." << std::endl;
length = lengthValue;
width = widthValue;
height = heightValue;
}
Box::Box() {} // No-arg constructor
// Function to calculate the volume of a box
double Box::volume()
{
return length*width*height;
}
int main()
{
Box firstBox {80.0, 50.0, 40.0}; // Create a box
double firstBoxVolume{firstBox.volume()}; // Calculate the box volume
std::cout << "Volume of Box object is" << firstBoxVolume << std::endl;
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。
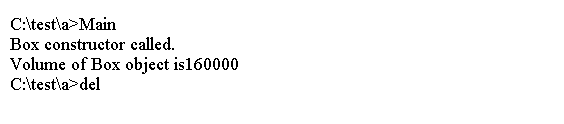
默认构造函数参数值
class Box {
private:
double length;
double width;
double height;
public:
// Constructors
Box(double lv = 1.0, double wv = 1.0, double hv = 1.0);
Box(); // No-arg constructor
double volume(); // Function to calculate the volume of a box
};

 国外主机测评 - 国外VPS,国外服务器,国外云服务器,测评及优惠码
国外主机测评 - 国外VPS,国外服务器,国外云服务器,测评及优惠码









