学习C++ – C++类
C++关键字类将代码标识为定义类的设计。
语法将Product标识为此类的类型名称。
设计类的第一步是提供类声明。
语法
类声明在声明之后被编码,并且可以包括数据成员和函数成员。
声明有一个私有部分,在该部分中声明的成员只能通过成员函数访问。
声明还有一个公共部分,声明的成员可以使用类对象直接由程序访问。
通常,数据成员进入私有部分,成员函数进入公共部分。
典型的类声明有这种形式。
class className {
private:
data member declarations
public:
member function prototypes
};
公共部分的内容构成了设计的抽象部分,公共接口。
在私有部分中封装数据保护数据的完整性,并称为数据隐藏。
类设计的第二步是实现类成员函数。
以下代码显示了如何使用成员函数定义类。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Printer {
public:
// function that displays a welcome message to the Printer user
void displayMessage() {
cout << "Welcome to the Grade Book!" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Printer myPrinter; // create a Printer object named myPrinter
myPrinter.displayMessage(); // call object"s displayMessage function
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

带参数的成员函数
以下代码显示了如何使用具有参数的成员函数定义类打印机,创建一个Printer对象并调用其displayMessage函数。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Printer {
public:
void displayMessage( string courseName )
{
cout << "Welcome to the grade book for\n" << courseName << "!"
<< endl;
}
};
// function main begins program execution
int main()
{
string nameOfCourse; // string of characters to store the course name
Printer myPrinter; // create a Printer object named myPrinter
cout << "Please enter the course name:" << endl;
getline( cin, nameOfCourse ); // read a course name with blanks
cout << endl; // output a blank line
myPrinter.displayMessage( nameOfCourse );
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

设置函数和获取函数
定义类包含一个courseName数据成员和成员函数来设置和获取其值;
使用这些函数创建和操作Course对象。
#include <iostream>
#include <string> // program uses C++ standard string class
using namespace std;
class Course {
public:
void setCourseName( string name ) {
courseName = name; // store the course name in the object
}
string getCourseName() {
return courseName; // return the object"s courseName
}
void displayMessage() {
cout << "Welcome to the grade book for\n" << getCourseName() << "!"
<< endl;
}
private:
string courseName; // course name for this Course
};
int main() {
string nameOfCourse; // string of characters to store the course name
Course myCourse; // create a Course object named myCourse
cout << "Initial course name is: " << myCourse.getCourseName()
<< endl;
cout << "\nPlease enter the course name:" << endl;
getline( cin, nameOfCourse ); // read a course name with blanks
myCourse.setCourseName( nameOfCourse ); // set the course name
cout << endl; // outputs a blank line
myCourse.displayMessage(); // display message with new course name
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

例子
此声明允许您声明产品类型的变量,称为对象或实例。
#include <string>
class Product {
private:
std::string company;
long shares;
double normal_val;
double discount_val;
void set_tot() { discount_val = shares * normal_val; }
public:
void acquire(const std::string & co, long n, double pr);
void buy(long num, double price);
void sell(long num, double price);
void update(double price);
void show();
};
例如,以下声明创建两个名为computer和toy的Product对象:
Product computer; Product toy;
您决定存储的信息在类数据成员中,如公司和股份。
例如,电脑公司持有该公司的名称,该股份成员持有Sally拥有的股份数量。
访问控制
私有和公共标签描述了类成员的访问控制。
任何使用特定类的对象的程序都可以直接访问公共部分。
程序只能通过使用public成员函数访问对象的私有成员。
例如,更改Product类的共享成员的唯一方法是使用Product成员函数之一。
公共成员函数作为程序和对象的私有成员之间的代理。
通过程序直接访问的数据绝缘称为数据隐藏。
类设计尝试将公共接口与实现细节分开。
类成员函数
以下代码显示了如何实现Product类。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Product // class declaration
{
private:
std::string company;
long shares;
double normal_val;
double discount_val;
void set_tot() { discount_val = shares * normal_val; }
public:
void acquire(const std::string & co, long n, double pr);
void buy(long num, double price);
void sell(long num, double price);
void update(double price);
void show();
};
void Product::acquire(const std::string & co, long n, double pr) {
company = co;
if (n < 0)
{
std::cout << "Number of shares can"t be negative; "
<< company << " shares set to 0.\n";
shares = 0;
}
else
shares = n;
normal_val = pr;
set_tot();
}
void Product::buy(long num, double price)
{
shares += num;
normal_val = price;
set_tot();
}
void Product::sell(long num, double price)
{
using std::cout;
shares -= num;
normal_val = price;
set_tot();
}
void Product::update(double price)
{
normal_val = price;
set_tot();
}
void Product::show()
{
std::cout << "Company: " << company
<< " Shares: " << shares << "\n"
<< " Share Price: $" << normal_val
<< " Total Worth: $" << discount_val << "\n";
}
#include <iostream>
int main(){
Product computer;
computer.acquire("NanoSmart", 20, 12.50);
computer.show();
computer.buy(15, 18.125);
computer.show();
computer.sell(400, 20.00);
computer.show();
computer.buy(300000,40.125);
computer.show();
computer.sell(300000,0.125);
computer.show();
return 0;
}
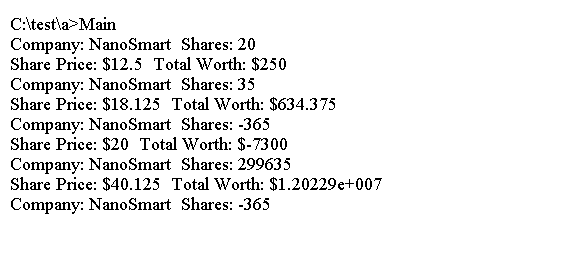
上面的代码生成以下结果。
内联方法
您可以在类声明之外定义一个成员函数,并将其内联。
为此,您只需在类实现部分中定义函数时使用内联限定符:
class Product
{
private:
...
void set_tot(); // definition kept separate
public:
...
};
inline void Product::set_tot() // use inline in definition
{
discount_val = shares * normal_val;
}

 国外主机测评 - 国外VPS,国外服务器,国外云服务器,测评及优惠码
国外主机测评 - 国外VPS,国外服务器,国外云服务器,测评及优惠码









