学习C++ – C++引用变量
C++引用是作为先前定义的变量的替代名称的名称。
例如,如果您使Bob成为Robert变量的引用,则可以互换使用Bob和Robert。
引用变量的主要用途是作为函数的形式参数。
如果使用引用作为参数,则该函数与原始数据而不是副本一起使用。
引用提供了一个方便的替代方法,用于处理具有函数的大型结构的指针。
创建引用变量
C和C++使用&符号来表示变量的地址。
C++使用&符号来声明引用。
例如,要使罗伯特成为变量的替代名称,您可以执行以下操作:
int bob; int & robert = bob; // makes robert an alias for bob
在这种情况下,&不是地址运算符。
相反,它作为类型标识符的一部分。
int& 表示引用到内部。
参考声明允许您互换使用bob和robert。
两者都是指相同的值和相同的内存位置。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int bob = 101;
int & robert = bob; // robert is a reference
cout << "bob = " << bob;
cout << ", robert = " << robert << endl;
robert++;
cout << "bob = " << bob;
cout << ", robert = " << robert << endl;
cout << "bob address = " << &bob;
cout << ", robert address = " << &robert << endl;
return 0;
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

注意
& 在下面的代码中声明一个引用类型变量。
int & robert = bob;
&运算符在下一个语句中是地址运算符:
cout <<", robert address = " << &robert << endl;
每一次递增robert影响这两个变量。
我们可以创建一个引用和一个指针来引用bob:
int bob = 101; int & robert = bob; // robert a reference int * pbob = &bob; // pbob a pointer
那么你可以用bob和bbo来表示robert和* pbob,并且可以和&bob互换使用表达式&robert和pbob。
我们必须在声明时初始化引用。
一个引用就像一个const指针,你必须在创建它时初始化它。
int & robert = bob;
实质上是一个这样的变相符号:
int * const pr = &bob;
在这里,引用robert与表达式*pr起着相同的作用。
引用作为函数参数
引用通常用作函数参数,使函数中的变量名称成为变量的别名。
这种传递参数的方法称为传递引用。
以下代码显示了如何使用引用和指针进行交换。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swapr(int & a, int & b); // a, b are aliases for ints
void swapp(int * p, int * q); // p, q are addresses of ints
int main(){
int my_value1 = 300;
int my_value2 = 350;
cout << "my_value1 = $" << my_value1;
cout << " my_value2 = $" << my_value2 << endl;
cout << "Using references to swap contents:\n";
swapr(my_value1, my_value2); // pass variables
cout << "my_value1 = $" << my_value1;
cout << " my_value2 = $" << my_value2 << endl;
cout << "Using pointers to swap contents:\n";
swapp(&my_value1, &my_value2); // pass addresses of variables
cout << "my_value1 = $" << my_value1;
cout << " my_value2 = $" << my_value2 << endl;
return 0;
}
void swapr(int & a, int & b) // use references
{
int temp;
temp = a; // use a, b for values of variables
a = b;
b = temp;
}
void swapp(int * p, int * q) // use pointers
{
int temp;
temp = *p; // use *p, *q for values of variables
*p = *q;
*q = temp;
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。
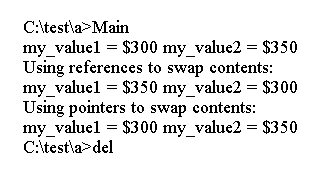
使用引用与类对象
C++通过引用将类对象传递给函数。
例如,您将使用字符串,ostream,istream,ofstream和ifstream类作为参数的引用参数。
以下代码使用字符串类。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
string my_func(const string & s1, const string & s2);
int main(){
string input;
string copy;
string result;
cout << "Enter a string: ";
getline(cin, input);
copy = input;
cout << "Your string as entered: " << input << endl;
result = my_func(input, "***");
cout << "Your string enhanced: " << result << endl;
cout << "Your original string: " << input << endl;
return 0;
}
string my_func(const string & s1, const string & s2){
string temp;
temp = s2 + s1 + s2;
return temp;
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。


 国外主机测评 - 国外VPS,国外服务器,国外云服务器,测评及优惠码
国外主机测评 - 国外VPS,国外服务器,国外云服务器,测评及优惠码









