Java面向对象设计 – Java注释反射
程序元素上的注释是Java对象。
允许您访问其注释的程序元素实现java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement接口。
以下类实现了AnnotatedElement接口:
AnnotatedElement接口的方法用于访问以下列出的对象类型的注释。
java.lang.Class java.lang.reflect.Executable java.lang.reflect.Constructor java.lang.reflect.Field java.lang.reflect.Method java.lang.reflect.Parameter java.lang.Package java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject
注释类型必须使用运行时的保留策略通过保留元注释注释,以便在运行时访问它。
例子
假设你有一个Test类,并且你想打印它的所有注释。以下代码片段将打印Test类的类声明上的所有注释:
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Deprecated
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] argv) {
// Get the class object reference
Class<Main> c = Main.class;
// Get all annotations on the class declaration
Annotation[] allAnns = c.getAnnotations();
System.out.println("Annotation count: " + allAnns.length);
// Print all annotations
for (Annotation ann : allAnns) {
System.out.println(ann);
}
}
}

Annotation接口的toString()方法返回注释的字符串表示形式。
例2
以下代码显示了如何获取特定注释。
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@interface Version {
int major();
int minor();
}
@Version(major=1,minor=2)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] argv) {
Class<Main> c = Main.class;
Version v = c.getAnnotation(Version.class);
if (v == null) {
System.out.println("Version annotation is not present.");
} else {
int major = v.major();
int minor = v.minor();
System.out.println("Version: major=" + major + ", minor=" + minor);
}
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

例3
以下代码显示了如何访问方法的注释。
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Version {
int major();
int minor();
}
@Version(major = 1, minor = 0)
class AccessAnnotation {
@Version(major = 1, minor = 1)
public void testMethod1() {
}
@Version(major = 1, minor = 2)
@Deprecated
public void testMethod2() {
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<AccessAnnotation> c = AccessAnnotation.class;
System.out.println("Annotations for class:" + c.getName());
printAnnotations(c);
System.out.println("Method annotations:");
Method[] m = c.getDeclaredMethods();
for (int i = 0; i < m.length; i++) {
System.out.println("Annotations for method:" + m[i].getName());
printAnnotations(m[i]);
}
}
public static void printAnnotations(AnnotatedElement programElement) {
Annotation[] annList = programElement.getAnnotations();
for (int i = 0; i < annList.length; i++) {
System.out.println(annList[i]);
if (annList[i] instanceof Version) {
Version v = (Version) annList[i];
int major = v.major();
int minor = v.minor();
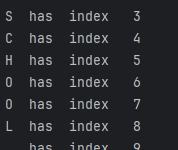
System.out.println("Found Version annotation: " + "major =" + major
+ ", minor=" + minor);
}
}
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

例4
以下代码显示了如何在运行时访问可重复注释的实例。
import java.lang.annotation.Repeatable;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface LogHistory {
Log[] value();
}
@Repeatable(LogHistory.class)
@interface Log {
String date();
String comments();
}
@Log(date = "02/01/2014", comments = "A")
@Log(date = "01/22/2014", comments = "B")
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<Main> mainClass = Main.class;
Log[] annList = mainClass.getAnnotationsByType(Log.class);
for (Log log : annList) {
System.out.println("Date=" + log.date() + ", Comments=" + log.comments());
}
Class<LogHistory> containingAnnClass = LogHistory.class;
LogHistory logs = mainClass.getAnnotation(containingAnnClass);
for (Log log : logs.value()) {
System.out.println("Date=" + log.date() + ", Comments=" + log.comments());
}
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。
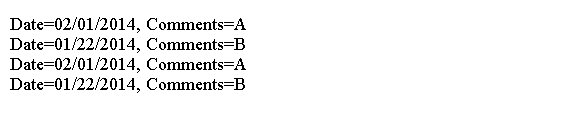

 国外主机测评 - 国外VPS,国外服务器,国外云服务器,测评及优惠码
国外主机测评 - 国外VPS,国外服务器,国外云服务器,测评及优惠码