Java格式 – Java日期格式模式
SimpleDateFormat日期和时间格式由日期和时间模式字符串指定。
在格式字符串中,从“A”到“Z”和从“a”到“z”被视为表示日期或时间字符串的组成部分的格式字母。
文本可以使用单引号(“)引用,以避免解释。“”表示单引号。 所有其他字符不解释并且将被简单地复制到输出字符串中。
模式
定义了以下模式字母:
| 字母 | 日期或时间组件 | 例子 |
|---|---|---|
G |
时代指示符 | AD |
y |
年 | 2014; 14 |
Y |
周年 | 2014; 14 |
M |
年份中的月份(上下文相关) | July; Jul; 07 |
L |
每年的月份(独立形式) | July; Jul; 07 |
w |
每年的一周 | 27 |
W |
每月一周 | 2 |
D |
每年的一天 | 189 |
d |
月份日 | 10 |
F |
每月的星期几 | 2 |
E |
周的名称 | Tuesday; Tue |
u |
周数(1 =星期一,…,7 =星期日) | 1 |
a |
Am/pm标记 | PM |
H |
时段(1-23) | 0 |
k |
时段(1-24) | 24 |
K |
上午/下午时间(0-11) | 0 |
h |
上午/下午时间(1-12) | 12 |
m |
分钟,小时 | 30 |
s |
第二分钟 | 55 |
S |
毫秒 | 978 |
z |
时区 | Pacific Standard Time; PST; GMT-08:00 |
Z |
时区 | -0800 |
X |
时区 | -08; -0800; -08:00 |
例子
下表有一些示例格式字符串及其结果。
| 日期和时间模式 | 结果 |
|---|---|
"yyyy.MM.dd G "at" HH:mm:ss z" |
2014.08.04 AD at 12:08:56 PDT |
"EEE, MMM d, ""yy" |
Wed, Jul 4, "01 |
"h:mm a" |
11:08 PM |
"hh "o""clock" a, zzzz" |
12 o"clock PM, Pacific Daylight Time |
"K:mm a, z" |
0:08 PM, PDT |
"yyyyy.MMMMM.dd GGG hh:mm aaa" |
02014.July.04 AD 12:08 PM |
"EEE, d MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss Z" |
Wed, 4 Jul 2001 12:08:56 -0700 |
"yyMMddHHmmssZ" |
020704120856-0700 |
"yyyy-MM-dd"T"HH:mm:ss.SSSZ" |
2014-07-04T12:08:56.235-0700 |
"yyyy-MM-dd"T"HH:mm:ss.SSSXXX" |
2014-07-04T12:08:56.235-07:00 |
"YYYY-"W"ww-u" |
2014-W27-3 |
例2
我们可以将字面量嵌入格式化的日期。
我们需要将它们放在单引号中以将它们作为文字。
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.GregorianCalendar;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GregorianCalendar gc = new GregorianCalendar(2010, Calendar.SEPTEMBER,9);
Date birthDate = gc.getTime();
String pattern = ""I was born on the day" dd "of the month "MMMM "in" yyyy";
SimpleDateFormat simpleFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat(pattern);
System.out.println(simpleFormatter.format(birthDate));
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

解析字符串到日期
我们可以使用parse()方法将String值转换为日期时间值 SimpleDateFormat 类。
parse()方法的签名如下:
public Date parse(String text, ParsePosition startPos)
parse()方法接受两个参数。text是要解析的字符串,startPos设置文本中字符从您要开始解析的位置开始的位置。
例3
以下代码显示如何将字符串解析为日期值。
import java.text.ParsePosition;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String text = "09/19/2014";
// Create a pattern for the date text "09/19/2014"
String pattern = "MM/dd/yyyy";
SimpleDateFormat simpleFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat(pattern);
// a ParsePosition object with value zero
ParsePosition startPos = new ParsePosition(0);
// Parse the text
Date parsedDate = simpleFormatter.parse(text, startPos);
System.out.println(parsedDate);
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

例4
以下代码解析单个字符串中的两个日期值。
import java.text.ParsePosition;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String text = "ab01/01/1999cd12/31/2000ef";
String pattern = "MM/dd/yyyy";
SimpleDateFormat simpleFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat(pattern);
// Set the start index at 2
ParsePosition startPos = new ParsePosition(2);
// Parse the text to get the first date (January 1, 1999)
Date firstDate = simpleFormatter.parse(text, startPos);
System.out.println(firstDate);
//Now, startPos has its index set after the last character of the first date parsed.
int currentIndex = startPos.getIndex();
System.out.println(currentIndex);
// To set its index to the next date increment its index by 2.
int nextIndex = currentIndex + 2;
startPos.setIndex (nextIndex);
// Parse the text to get the second date (December 31, 2000)
Date secondDate = simpleFormatter.parse(text, startPos);
System.out.println(secondDate);
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。

例5
以下代码显示如何解析时间戳以获取时间零件
import java.text.ParsePosition;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "2014-05-04 09:10:40.321";
// Prepare the pattern
String pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(pattern);
// Parse the text into a Date object
Date dt = sdf.parse(input, new ParsePosition(0));
System.out.println(dt);
// Get the Calendar instance
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.setTime(dt);
// Print time parts
System.out.println("Hour:" + cal.get(Calendar.HOUR));
System.out.println("Minute:" + cal.get(Calendar.MINUTE));
System.out.println("Second:" + cal.get(Calendar.SECOND));
System.out.println("Millisecond:" + cal.get(Calendar.MILLISECOND));
}
}
上面的代码生成以下结果。
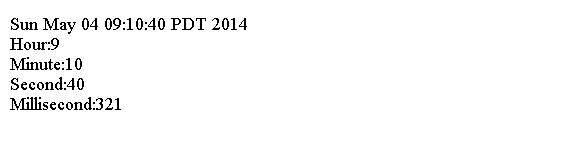

 国外主机测评 - 国外VPS,国外服务器,国外云服务器,测评及优惠码
国外主机测评 - 国外VPS,国外服务器,国外云服务器,测评及优惠码